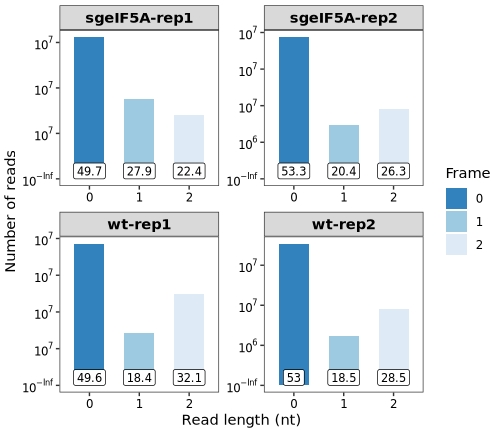
frame_plot(obj0)5 In frame ratio
5.1 Reading Frame and Quality Assessment in Ribo-seq
Ribosome profiling (Ribo-seq) is a powerful technique to study translation in vivo by sequencing the protected mRNA fragments (RPFs, Ribosome-Protected Fragments) associated with translating ribosomes. One hallmark of high-quality Ribo-seq data is the strong 3-nucleotide (nt) periodicity observed in coding sequences (CDS), reflecting the triplet codon structure recognized by translating ribosomes.
5.1.1 What is “Reading Frame” in Ribo-seq?
In Ribo-seq data analysis, each RPF can be assigned to a reading frame based on its P-site position relative to the annotated coding region:
Frame 0: Aligned with the annotated coding frame (i.e., P-site at the first nucleotide of a codon)
Frame 1: Offset by +1 nt from frame 0
Frame 2: Offset by +2 nt from frame 0
5.1.2 In-frame ratio: A key quality metric
A well-annotated and high-quality Ribo-seq experiment typically shows a clear enrichment of reads in frame 0 within annotated CDS regions. This behavior is quantified by the in-frame ratio, which measures the proportion of reads that fall into frame 0 among all reads mapping to coding regions.
A strong in-frame signal indicates:
Accurate P-site offset calibration
High signal-to-noise ratio (i.e., true ribosome-derived footprints dominate)
Proper rRNA/tRNA depletion and library preparation
Tip: In-frame ratio is best evaluated on well-expressed coding sequences to avoid sampling noise from low-coverage genes.
5.1.3 To check frame periodicity:
You can use visualization tools (e.g., metagene analysis, frame_length plots) or frame-specific coverage summaries to assess periodicity. Some Ribo-seq analysis packages provide automatic frame bias summaries for quick evaluation.
5.2 Periodicity plot
The frame_plot() function can be used to evaluate and visualize the overall distribution of reads across the three reading frames (0, 1, and 2) in a sample:
This plot helps assess the quality of Ribo-seq data by revealing frame-specific read enrichment—ideally showing a strong bias toward frame 0 in coding regions, which reflects good 3-nt periodicity.